A business owner or firm may need to know the value of a business for a variety of reasons, including when the time comes to sell or buy a business, settle a legal dispute, restructure capital, expand a business, etc. A qualified valuation professional with the necessary credentials should perform the in-depth financial analysis that is necessary for business valuation. Small business owners that opt for a free business assessment drastically undervalue the benefits they stand to gain from a thorough valuation investigation and expert valuation report. These advantages assist business owners in negotiating a strategic sale of their company to obtain a fair price, reduce the management’s financial risk in a legal proceeding, etc.


Information covered in our business valuation report
These elements will be covered in our appraisal report:
- Financial projections and Fund Utilization Strategies
- Company Profile and Promoter Background;
- Industry Outlook & Geographic Prospectus
- Proposed Market Penetration Strategies
- ROI and Other Relevant Financial Parameters for Prospectus Evaluation
- Valuation of Business and Key Evaluation Parameters
- Conclusion
There are just three valuation methodologies, even if there are many valuation models and indicators available:
Internal assessment
It connects an asset’s value to its intrinsic qualities, including its ability to produce cash flows and the risk associated with those cash flows. When cash flows are more predictable for the business, intrinsic value is most often calculated using a discounted cash flow valuation, where the value of an asset equals the present value of anticipated future cashflows on that asset.
Comparative valuing
By comparing the prices of “similar” assets to a common variable, such as earnings, cashflows, book value, or sales, it calculates the value of an asset.
Value of contingent claims
To calculate the value of assets that share option characteristics, it uses option pricing models.
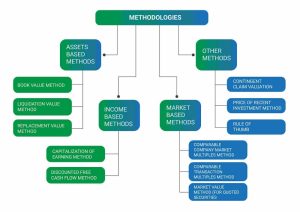
Based on the three methodologies mentioned above, there are three primary ways and additional techniques to evaluate the worth of business practice:
- Asset techniques: To determine the worth of the entire business enterprise, the asset approach to business valuation takes into account the underlying business assets. This method is based on the substitution economic concept and aims to calculate the costs of re-creating a company of equivalent economic usefulness, that is, a company that can generate the same returns for its owners as the subject company.
The asset approach’s company valuation techniques include:
- The book value method.
- Replacement value method
- Liquidation value method
- Market technique: According to the market approach to business valuation, one looks to the market for cues as to what a company is worth. Most frequently, sales of businesses that are similar to the one being analyzed are examined to get comparative data that may be utilized to calculate the subject business’s value. This strategy makes advantage of the economic principle of competition, which aims to determine the worth of a company by comparing it to others of a similar nature whose value has previously been determined by the market.
The market approach business valuation techniques include:
- Comparative company market multiple approaches
- Comparable transactions using various techniques
- Market value approaches (Quoted securities)
- Income sources: The income approach to business valuation bases its assessment of a company’s value on the economic idea of expectation. To achieve this, one makes projections of the future profits the company owners can anticipate from the in-focus enterprise. The risk involved in getting them fully and on time is then compared to these returns.
The returns are projected as either a one-time sum or as a future stream of income for the company’s owners. Following that, the risk is measured using what is known as capitalization or discount rates. Direct capitalization strategies are those that rely on a single indicator of business earnings. The discounting methods are those that make use of a stream of revenue. The worth of the commercial enterprise is determined as the present value of the anticipated income stream using discounting procedures, which directly account for the time value of money.
The Income Approach includes the following methods:
- Discounted Cash Flow Method
- Price to Earnings or Earnings Multiples or Capitalizing Earnings Methods
- Other Methods: Other approaches to corporate appraisal include the following:
- Valuing contingent claims
- Cost of a recent investment strategy
- Rule of thumb
The same object may be valued differently at the same moment using any of the aforementioned methods. We must be able to comprehend and use each technique to fully understand valuation. Each strategy has a proper time and place and knowing when to utilise each one is essential to mastering value. There isn’t a single, infallible method or approach for business appraisal. Therefore, using a variety of business valuation techniques under each methodology is standard practice. The business value is then calculated by comparing the outcomes of the chosen methodologies. Typically, each business valuation method’s output is given a weighting. The worth of the analysed business is then calculated using the sum of the weighted results.
Business valuation refers to the process of determining the present worth of a firm and there are various approaches used to determine value. Fair market value is frequently used as the standard of value. The fair market value is the price at which a business would be sold between two independent parties who each had the necessary knowledge and information, were not the subject of any undue pressure, and had access to all the data necessary to make an informed choice. When valuing a firm, an analyst considers factors such as management, capital structure makeup, expected future earnings, the market value of assets, etc.
It is a common mistake to say that the value of a company is a multiple of EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization) because it does not take into account industry, business risks, expected cash flows, debts, etc. Therefore, it is always recommended to have a business valuation done by a valuation specialist. Without knowing the true fair market value of the business, the trader may sell the business for less or buy for its true value. For these reasons, a business appraisal can be a good investment. Sometimes millions can be saved by paying the right price or making the right decision not to invest in a bad business.